Single Girder VS Double Girder Overhead Cranes: Which Is Right For You?
January 31, 2024
 Overhead cranes play a crucial role in modern industry, serving as the backbone of material handling. Especially in various manufacturing workshops, these cranes ensure the smooth lifting and transportation of heavy loads. They not only significantly improve work efficiency but also ensure the safety of the workplace. Among various types of overhead cranes, single girder and double girder bridge cranes have attracted considerable attention due to their unique features and applications. Understanding their functions and suitability is crucial for making informed decisions when selecting the appropriate lifting solution. This article will delve into the comparison between single girder and double girder overhead cranes, helping you make wise decisions amidst numerous choices.
Overhead cranes play a crucial role in modern industry, serving as the backbone of material handling. Especially in various manufacturing workshops, these cranes ensure the smooth lifting and transportation of heavy loads. They not only significantly improve work efficiency but also ensure the safety of the workplace. Among various types of overhead cranes, single girder and double girder bridge cranes have attracted considerable attention due to their unique features and applications. Understanding their functions and suitability is crucial for making informed decisions when selecting the appropriate lifting solution. This article will delve into the comparison between single girder and double girder overhead cranes, helping you make wise decisions amidst numerous choices.
What is a Single Girder Overhead Crane?
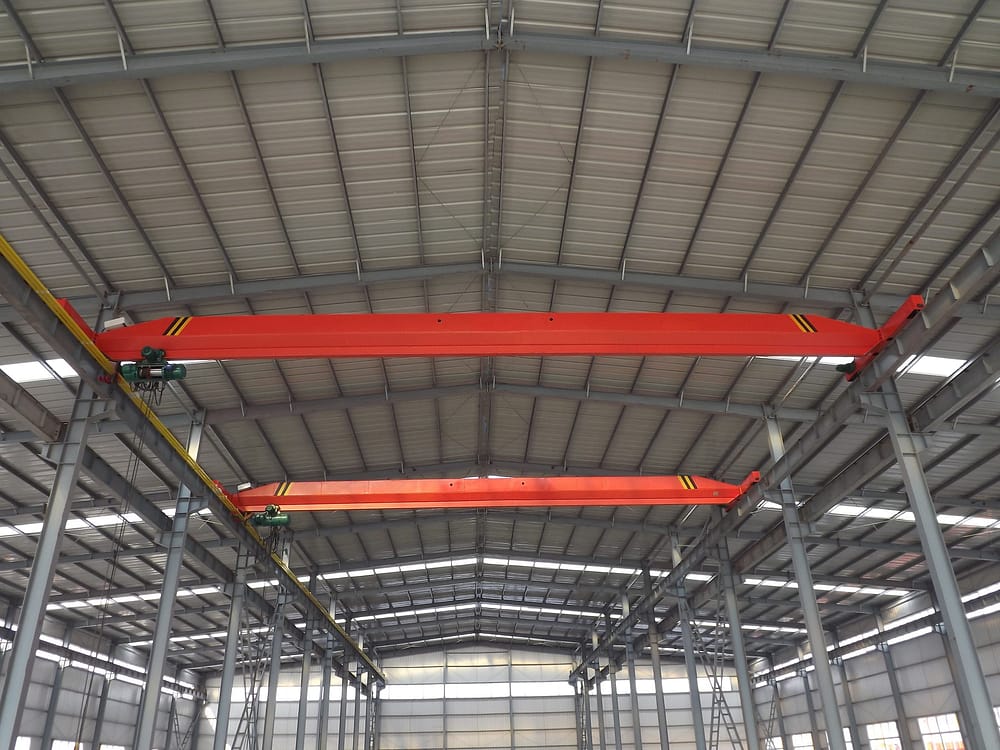 A single girder overhead crane is a lifting machinery consisting of a single main girder, known for its simple and efficient design. This type of crane typically includes a beam spanning the workshop, with a running mechanism underneath for lateral movement of heavy loads. Equipped with wheels at its ends, the crane can move along tracks, facilitating material transport throughout the entire working area. The simplified structure of a single girder bridge crane is cost-effective in both manufacturing and maintenance.
A single girder overhead crane is a lifting machinery consisting of a single main girder, known for its simple and efficient design. This type of crane typically includes a beam spanning the workshop, with a running mechanism underneath for lateral movement of heavy loads. Equipped with wheels at its ends, the crane can move along tracks, facilitating material transport throughout the entire working area. The simplified structure of a single girder bridge crane is cost-effective in both manufacturing and maintenance.
Advantages and Applications of Single Girder Overhead Cranes
Single girder cranes are particularly suitable for scenarios with light to medium loads, such as small factories, warehouses, and specific production lines. Their design makes them ideal for environments with limited space or a need for rapid material movement. The main advantages lie in their lightweight structure, making installation and operation relatively simple while effectively reducing energy consumption.Limitations and Scope of Single Girder Overhead Cranes
Despite various advantages, single girder bridge cranes have limitations. Due to their structural design, they are generally unsuitable for handling extremely heavy loads or complex lifting tasks. Their operating speed and lifting height may be lower compared to more complex double girder systems. Additionally, when high stability and load-carrying capacity are crucial in the working environment, single girder EOT cranes may fall short of meeting these requirements. Therefore, understanding the scope and limitations is crucial before choosing a single girder crane.What is a Double Girder Overhead Crane?
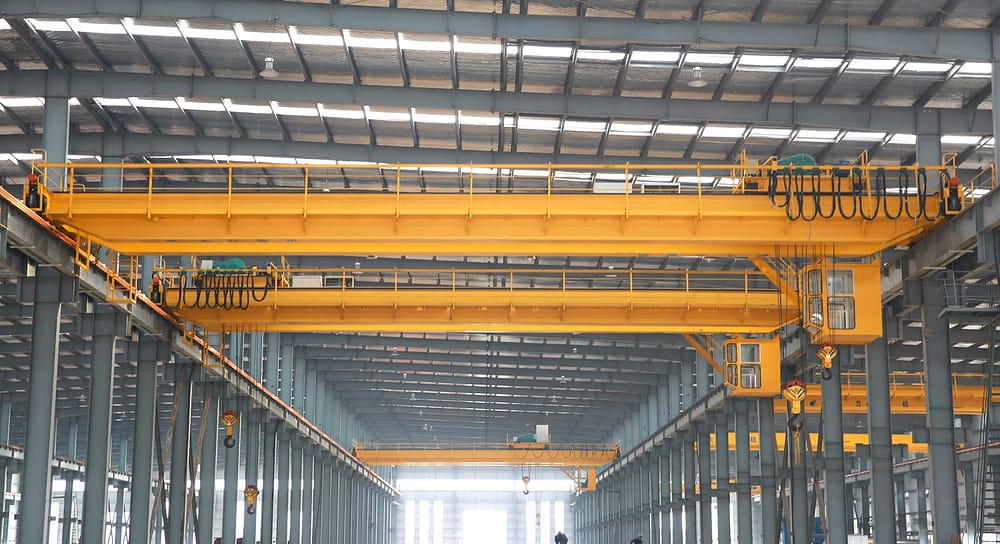 A double girder overhead crane is composed of two parallel main girders, providing additional support and stability. This design allows the crane to carry heavier loads while maintaining a robust and durable structure. Double girder bridge cranes are typically equipped with more sophisticated lifting and running mechanisms, enabling operation over a wider range. Compared to single girder cranes, the double girder design allows for higher lifting speeds and larger spans, covering a larger working area.
A double girder overhead crane is composed of two parallel main girders, providing additional support and stability. This design allows the crane to carry heavier loads while maintaining a robust and durable structure. Double girder bridge cranes are typically equipped with more sophisticated lifting and running mechanisms, enabling operation over a wider range. Compared to single girder cranes, the double girder design allows for higher lifting speeds and larger spans, covering a larger working area.
Advantages and Applications of Double Girder Overhead Cranes
Double girder bridge cranes are indispensable in heavy industries, especially in environments requiring high load capacity and stability, such as large manufacturing plants, heavy industrial workshops, docks, and storage facilities. Their main advantages lie in the ability to handle heavy materials safely and efficiently, providing higher operational efficiency. The design of double girder EOT cranes allows them to operate over longer spans without sacrificing performance or safety.Limitations and Scope of Double Girder Overhead Cranes
While double girder bridge cranes excel in performance, their complex design comes with higher costs, including installation, operation, and maintenance. Due to their weight and size, double girder cranes may require stronger support structures and larger working spaces. Additionally, compared to single girder designs, adjustments and repairs for double girder overhead cranes may be more complex and time-consuming. Therefore, for occasions that do not require frequent or heavy-duty material handling, the more economical and flexible single girder crane might be considered. Balancing the performance advantages and potential costs is crucial when choosing the appropriate type of crane.Performance and Functionality Comparison
Primary Performance Comparison
Single girder and double girder overhead cranes exhibit key differences in design, performance, and application. Choosing between a single girder and double girder crane requires a comprehensive consideration of specific industrial applications, required lifting capacity, working environment, and budget, among other factors. Each type has its own advantages and characteristics, catering to different industrial needs. |
 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Single Girder Overhead Cranes | Double Girder Overhead Cranes |
| Lifting Capacity | 1~20 ton | 5~800 ton |
| Work Duty | A1~A5 | A3~A8 |
| Span Length | 7.5~31.5m | 10.5~40.5m |
| Lifting Height | 3.2~40m | 12~60m |
| Lifting Speed | 0.32~16 m/min | 0.63~63 m/min |
| Trolley Travelling Speed | 3.2~40 m/min | 10~63 m/min |
| Crane Travelling Speed | 3.2~50 m/min | 16~110 m/min |
| Work Environment Temperature | -20℃~+40℃ | -20℃~+50℃ |
Load Capacity
There is a significant difference in load capacity between single girder and double girder overhead cranes. Single girder cranes are typically designed for light to medium loads, with a carrying capacity ranging from approximately 1 ton to 20 tons. In contrast, double girder bridge cranes, due to their dual main beam structure, can handle heavier loads, typically ranging from 5 tons to 320 tons. The strength and stability of the double girder design make it an ideal choice for handling heavy materials. For special projects, custom heavy-duty overhead cranes with large tonnages, such as the four-girder overhead crane used in the Three Gorges Hydropower Station project in China, can have a carrying capacity of up to 1200 tons.Working Duty
Working duty is a classification standard in the field of overhead cranes, typically based on usage scenarios and job requirements. The working Duty signifies the design and performance of the crane, determining its reliability and safety under different operating conditions. Overhead cranes are generally classified into working duty A1 to A8, with each class representing different usage conditions and requirements. Choosing the appropriate working class for the bridge crane is crucial to ensuring smooth operations. A reasonable match of the working class can enhance the crane’s lifespan, work efficiency, and, most importantly, ensure safe operations. Single Girder Overhead Crane Working Duty Range: A1-A5. A1 is predominant for manual single girder bridge cranes, and A3 is common for electric single girder cranes, with the possibility of upgrading to A4 based on working conditions. European standard single girder cranes can achieve up to A5 class. Single girder EOT cranes are suitable for material handling in factory workshops and production lines, with designs and performance more suitable for light and medium loads. Double Girder Overhead Crane Working Duty Range: A3-A8. A5 and A6 are commonly used for electric magnetic double girder bridge cranes and grab bucket double girder cranes, with A6 being more prevalent. A7 is common for foundry cranes, and A8 is required for applications like double trolley double girder cranes in pipe pile production lines or A8 for waste handling cranes. These classes of cranes are common in heavy manufacturing industries such as steel mills, power plants, paper mills, and heavy construction projects. They possess greater load-carrying capacity and higher performance standards, capable of handling more complex and critical lifting tasks. Work EfficiencyWork Efficiency
In terms of work efficiency, while single girder cranes may have a lower lifting capacity compared to double girder EOT cranes, their lighter structural design makes them more agile when handling light loads. Double girder cranes, due to their stronger structural design, usually offer faster lifting and running speeds, resulting in overall higher efficiency. For instance, a 5-ton double girder bridge crane can achieve a maximum operating speed of up to 110 m/min, which is crucial for applications requiring rapid movement of large or heavy materials, such as in centrifuge span in pipe pile production lines or waste-to-energy plants.Price Comparison
The price difference between single girder and double girder overhead cranes is primarily influenced by various factors such as their design, load-carrying capacity, materials, configuration, and differences in applications. The table below provides a comparison reference for the prices of three common tonnages of bridge cranes: single girder bridge crane, double girder bridge crane with hoist trolley, and double girder bridge crane with winch, all with a span of 19m and a lifting height of 6 meters. Crane prices may vary based on market fluctuations, and the prices provided below are for reference only. |
 |
 |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Lifting Capacity | Single Girder Overhead Crane | Double Girder Overhead Crane with Hoist Trolley | Double Girder Overhead Crane with Winch Trolley |
| 1t | $3,325 | — | — |
| 2t | $3,925 | — | — |
| 3t | $4,355 | — | — |
| 5t | $4,765 | $12,180 | $22,750 |
| 10t | $6,625 | $13,950 | $25,080 |
| 15t | $7,896 | $18,000 | $32,390 |
| 20t | $11,350 | $23,900 | $33,850 |
| 32t | — | $27,870 | $47,650 |
Space Utilization Comparison
Regarding space utilization, single girder cranes are particularly suitable for scenarios with limited space due to their smaller size and lightweight design. Their streamlined design allows for maximizing the workshop height, making them suitable for material handling in low-ceiling buildings. On the other hand, double girder cranes, with larger dimensions and weight, typically require more significant installation space and higher building structures, making them suitable for large industrial applications. When choosing the appropriate crane type, on-site space conditions and operational requirements must be considered. The lifting mechanism of single girder cranes primarily relies on electric hoists, which can be installed at the bottom, side, or top of the main beam. Especially in environments with space constraints or the need for maximum ground space utilization, single girder cranes offer multiple effective and economical lifting solutions.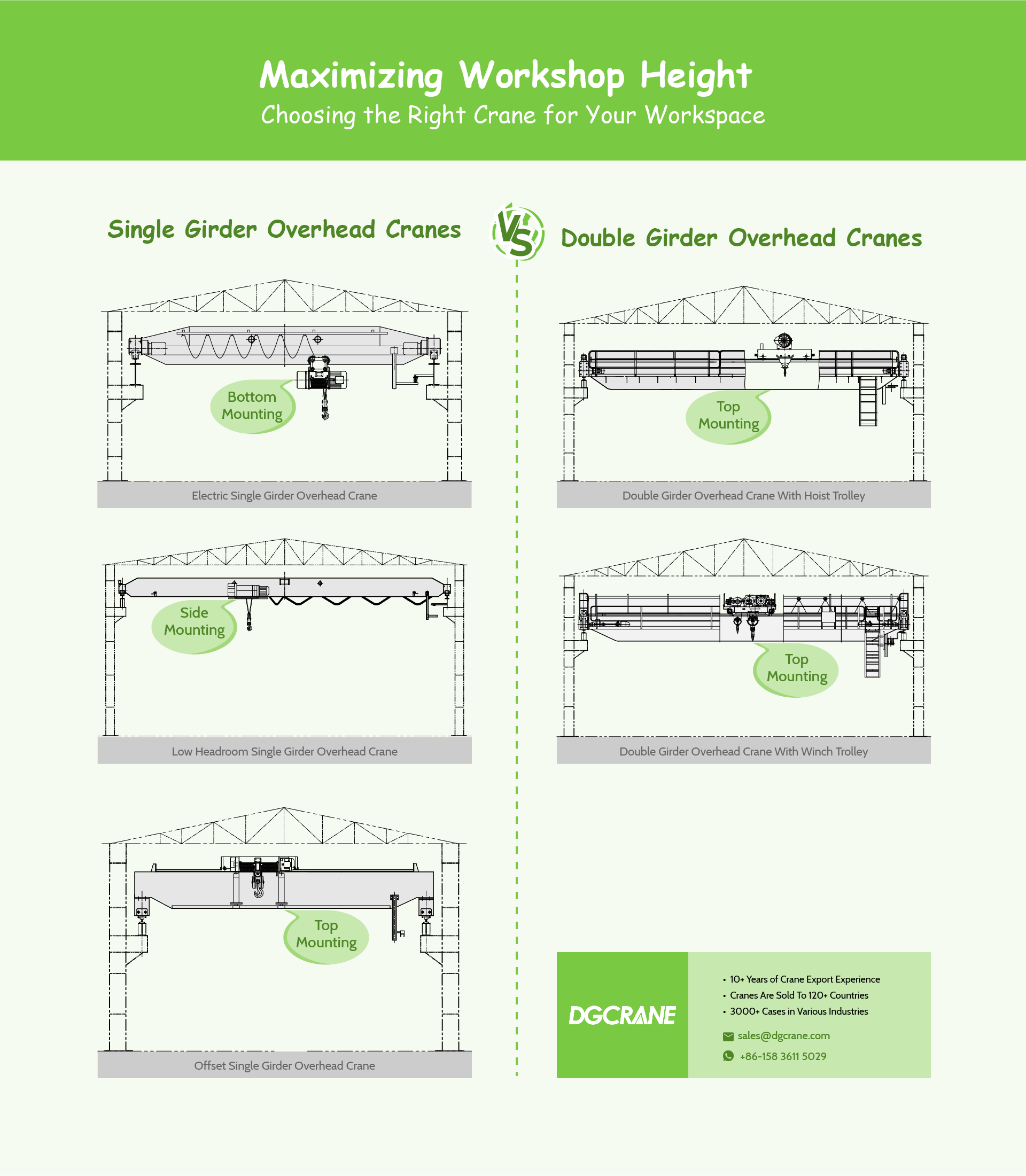
Various Types of Overhead Cranes Designed for Different Space Requirements:
LD Electric Single Girder Overhead Crane
The most widely used single girder crane with the hoist installed beneath the main beam. The main beam structure is typically an I-beam or box-type girder. This type of crane is chosen when there is sufficient lifting height space inside the factory, providing high overall cost-effectiveness.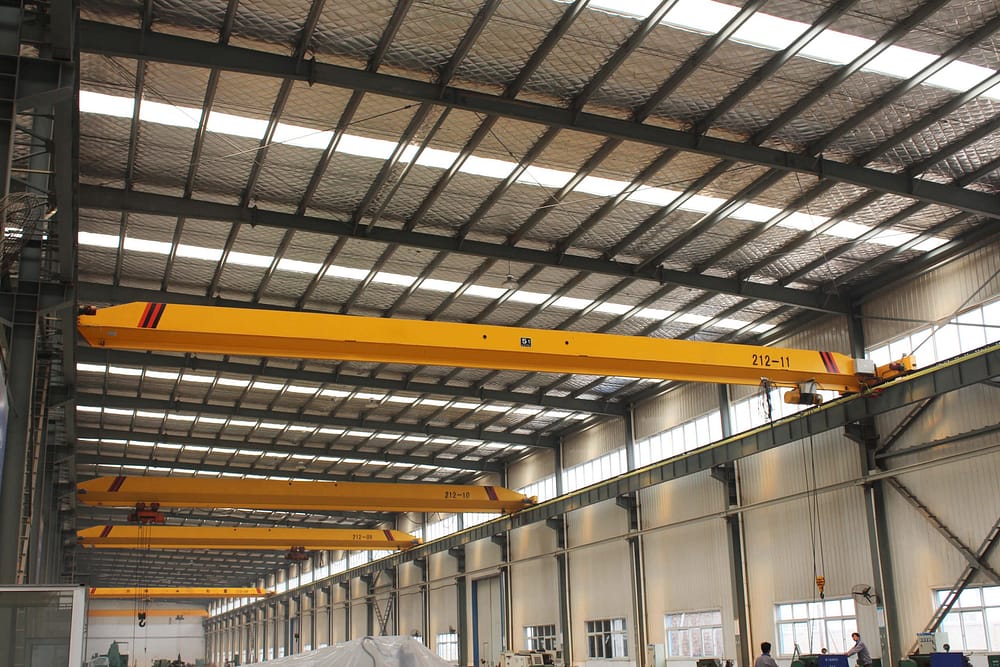
LDC Low Headroom Single Girder Overhead Crane
Design features: The main beam of the crane is often in the form of a square box-type structure. The wheels of the electric hoist’s traveling trolley can run back and forth on the lower flange of the main beam. The lifting mechanism uses a low headroom electric hoist. This design results in a lower overall height of the overhead crane, allowing it to operate in spaces with limited height. Space utilization advantage: It maximizes vertical space, particularly suitable for work areas with lower ceilings. By reducing the vertical space required by the crane itself, low headroom cranes provide greater lifting height, making them an ideal choice in places with height restrictions.
Space utilization advantage: It maximizes vertical space, particularly suitable for work areas with lower ceilings. By reducing the vertical space required by the crane itself, low headroom cranes provide greater lifting height, making them an ideal choice in places with height restrictions.
LDP Offset Single Girder Overhead Crane
Design features: A type of overhead crane with a trolley structure shaped like a triangle. The hoist trolley can be installed above the main beam of the crane.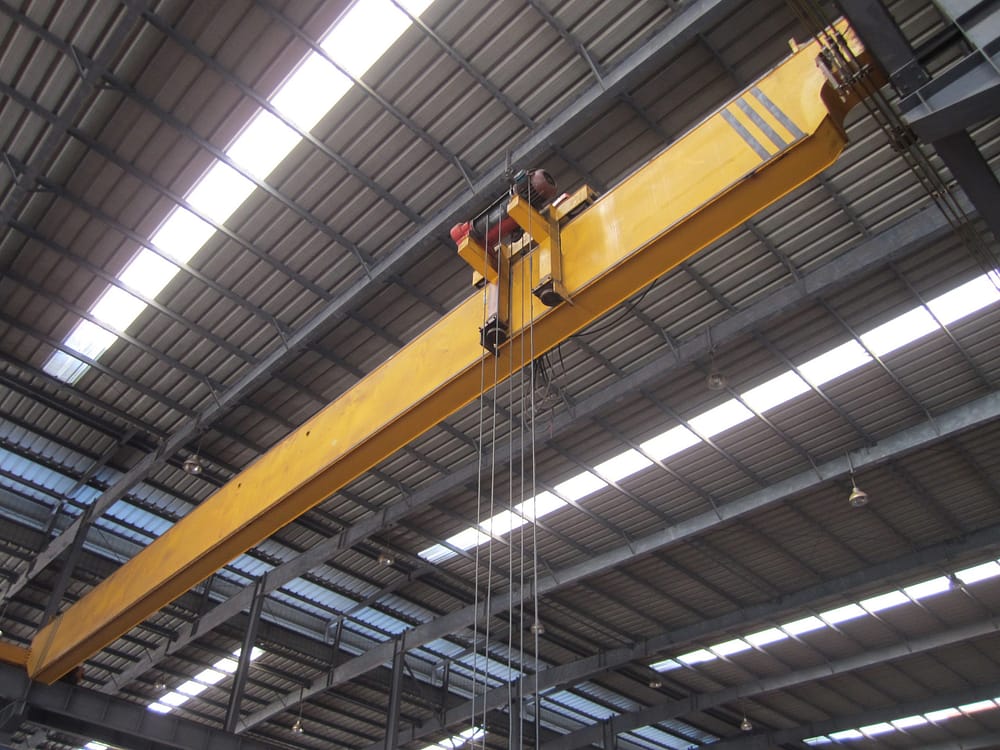 Space utilization advantage: This structure is commonly used in situations where the track height inside the factory is low, but there is significant net height between the track top surface and the lowest point of the factory. This structure better utilizes the height space within the workshop, effectively increasing the hoist’s lifting height.
Double Girder Overhead Cranes
Space utilization advantage: This structure is commonly used in situations where the track height inside the factory is low, but there is significant net height between the track top surface and the lowest point of the factory. This structure better utilizes the height space within the workshop, effectively increasing the hoist’s lifting height.
Double Girder Overhead Cranes
Double Girder Overhead Cranes
Double girder cranes typically have larger structural dimensions, and the lifting mechanism is often a hoist trolley or a winch-style trolley. The hoist trolley or winch-style lifting trolley is installed between two parallel main beams. This design allows the trolley to run above the main beam, providing greater lifting height. However, sufficient space must be reserved above the main beam for the trolley to operate. Double girder overhead cranes are suitable for applications requiring high lifting height and large load-carrying capacity but demand significant vertical space.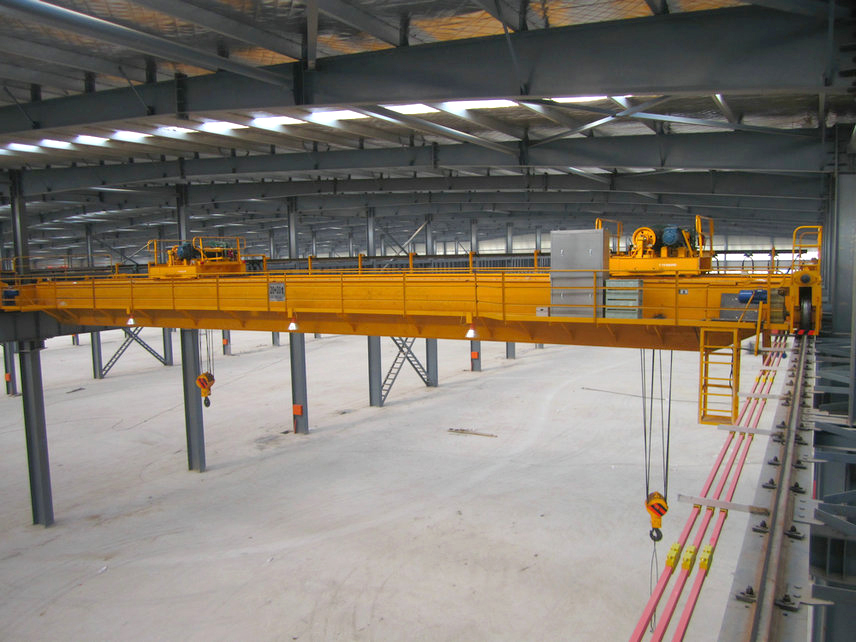 The choice between single girder and double girder bridge cranes should be based on specific industrial requirements, budget constraints, and long-term operational goals. When evaluating cost-effectiveness, considering both initial investment and long-term operational and maintenance costs is crucial.
The choice between single girder and double girder bridge cranes should be based on specific industrial requirements, budget constraints, and long-term operational goals. When evaluating cost-effectiveness, considering both initial investment and long-term operational and maintenance costs is crucial.
How to Choose the Right Bridge Crane According to Business Requirements
Selecting the appropriate bridge crane begins with a detailed assessment of business needs. This includes considerations for the required load capacity, the frequency of crane operation, characteristics of the work environment, and budget constraints. Key steps in this process include:- Clearly Define Load Requirements: Choose the type of bridge crane based on the maximum weight that needs to be lifted in daily operations.
- Evaluate Workspace: Select the most suitable bridge crane model based on the spatial constraints and height specifications of the work area.
- Consider Long-Term Costs and Benefits: Evaluate the economic aspects not only in terms of initial purchase costs but also regarding the long-term operation and maintenance expenses.
- Safety and Stability: Ensure that the selected bridge crane meets safety and stability standards applicable to the work environment. Consider factors that may pose risks during operations.
- Professional Consultation: Before making a final decision, seek advice from professional crane manufacturers or suppliers to obtain detailed information and personalized recommendations.
Case Study Comparison
In a large welding assembly workshop of a chemical equipment manufacturing plant, there is an existing QD double girder bridge crane with a capacity of 16 tons, a span of 19.5 meters, A5 working class, and a lifting height of 12 meters. Due to the expansion of production capacity, the maximum weight of finished welded components needs to be increased from the original 12 tons to 25 tons, requiring an upgrade and modification of the lifting equipment in the workshop.Workshop Conditions:
Net clearance height from the top surface of the main crane rail to the lowest point in the factory is 2450mm. Maximum weight of finished welded components: 25 tons, length 11800mm, diameter Φ3600mm (non-homogeneous structure). Maximum distance between columns: 6000mm; Maximum wheel pressure allowed for the crane beam is 192KN (per wheel). Actual lifting height required for workpieces during operation: 7200mm. Existing crane rail height from the top surface to the highest point of the crane is 2170mm; Maximum wheel pressure is 168KN (per wheel).Design Solution:
It is recommended to add a new 32-ton bridge crane, utilizing the existing columns and crane beams. The existing double girder bridge crane can be used for lifting other components in the workshop. Adding a single 16-ton crane would not facilitate coordinated operations with the original double girder crane, making it unsuitable for handling the maximum lifting weight requirements.Comparison of Proposed Solutions:
Lifting Solution One:
Two 16-ton standard single girder bridge cranes working in tandem. Working duty A3 (not suitable for heavy-duty operations). Not feasible due to the mismatch in the working class with the actual workshop conditions.Lifting Solution Two:
One 32-ton standard double trolley double girder bridge crane. Oversized wheel pressure, exceeding the maximum allowable value for the crane beam (192KN). Not suitable due to excessive wheel pressure and height requirements.Lifting Solution Three:
Two 16-ton European standard single girder bridge cranes working in tandem. Working duty A5, suitable installation dimensions, and wheel pressure. This scheme meets the installation size and wheel pressure requirements and is considered viable.Lifting Solution Four:
One 32-ton European standard double trolley double girder bridge crane. Working duty A5, suitable installation dimensions, and wheel pressure. This scheme also meets the installation size and wheel pressure requirements and is considered viable.Price Comparison:
Two 16-ton European standard single girder bridge cranes: $32,315 USD. One 32-ton European standard double trolley double girder bridge crane: $40,815 USD. The two 16-ton European Standard single girder overhead cranes are $8,500 USD cheaper than one 32-ton European standard double trolley double girder overhead crane.Recommended Solution:
Following discussions with the client, the recommended solution is as follows: We propose the adoption of two 16-ton European standard single girder electric overhead cranes with a span of 19.5m, a lifting height of 12m, and a working duty of A5. When lifting the largest finished welding components (or large welding components), a coordinated lifting operation can be achieved through the collaborative action of the two cranes. Compared to double girder bridge cranes, European standard single girder cranes offer advantages such as lighter weight, lower wheel pressure, lower clearance height, and full-vehicle variable frequency speed control.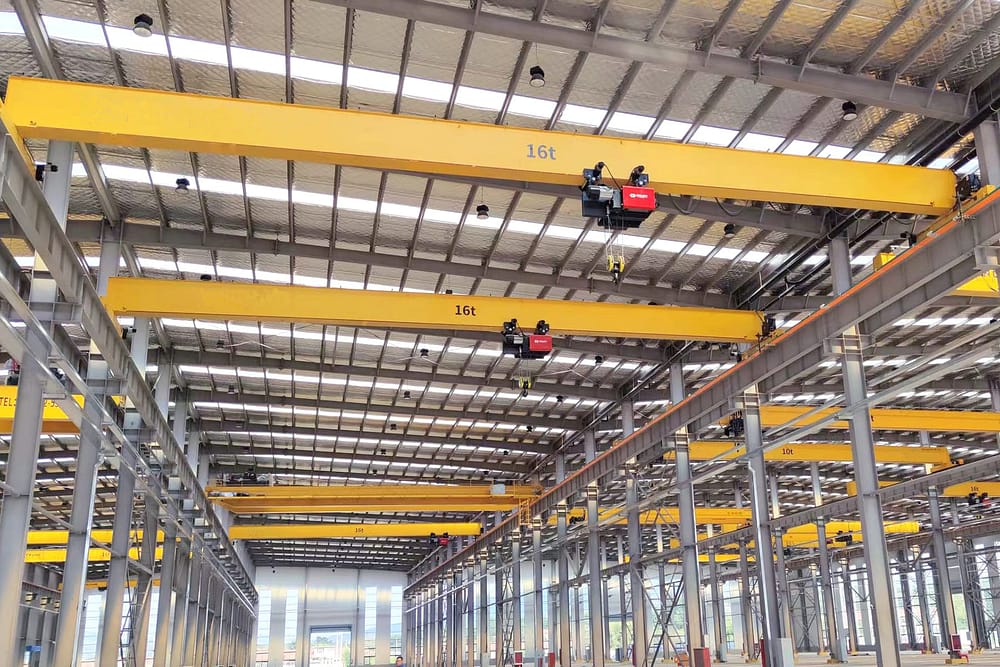 Especially during the joint operation of the two cranes, the wheel pressure on the crane’s main trolley is more evenly distributed, improving the load-bearing capacity of the crane beam system. This not only addresses the issue of insufficient load-bearing capacity in the old workshop but also meets the clearance height requirements for the overhead space above the crane rail. The overall speed control of the crane is achieved through variable frequency speed regulation, enhancing the safety and stability of equipment operation. The crane operates with low noise, minimal impact, smooth braking, and continuous acceleration and deceleration, contributing to favorable conditions for extending the crane’s service life.
In this proposed solution, the European standard single girder crane, in the same specifications as the double girder bridge crane, is not only more cost-effective but also exhibits superior stability and performance. It stands as a well-balanced solution, considering practicality, performance, and cost-effectiveness.
Especially during the joint operation of the two cranes, the wheel pressure on the crane’s main trolley is more evenly distributed, improving the load-bearing capacity of the crane beam system. This not only addresses the issue of insufficient load-bearing capacity in the old workshop but also meets the clearance height requirements for the overhead space above the crane rail. The overall speed control of the crane is achieved through variable frequency speed regulation, enhancing the safety and stability of equipment operation. The crane operates with low noise, minimal impact, smooth braking, and continuous acceleration and deceleration, contributing to favorable conditions for extending the crane’s service life.
In this proposed solution, the European standard single girder crane, in the same specifications as the double girder bridge crane, is not only more cost-effective but also exhibits superior stability and performance. It stands as a well-balanced solution, considering practicality, performance, and cost-effectiveness.
Single Girder Crane vs. Double Girder Crane: A Comparative Summary
Determining Load Capacity:
Choose the crane’s load capacity based on the typical weight of materials lifted in the working environment. Single girder cranes are suitable for light to moderate loads, while double girder cranes are preferable for heavy-duty applications.Considering Space Limitations:
Evaluate the size and shape of the working area. Single girder cranes are ideal for smaller spaces or limited clearance heights, while double girder cranes are suitable for larger work areas.Budget and Cost-Effectiveness:
Consider both initial purchase costs and long-term maintenance and operational expenses. Single girder cranes are generally more economical in terms of initial purchase and maintenance costs. Although double girder cranes have higher upfront costs, they offer superior long-term efficiency and stability.Safety and Stability:
Take into account the required safety levels and stability. Double girder cranes provide higher stability and safety, especially when handling heavy loads.Operation and Maintenance:
Single girder cranes are characterized by simple operation and easy maintenance, whereas double girder cranes may require more specialized operation and maintenance expertise. Single girder cranes are particularly suitable for scenarios with light to medium loads, while double girder cranes are indispensable in heavy industries, especially when high load capacity and stability are required. Choosing the right crane is crucial for enhancing industrial productivity, ensuring operational safety, and optimizing long-term return on investment. It is essential to make a wise decision based on specific operational conditions and financial budgets, considering comprehensive factors.Consultation with Crane Industry Professionals for Informed Decisions
When faced with the task of selecting the appropriate overhead crane, understanding the specific advantages and application scenarios of single girder and double girder cranes is crucial. To ensure that your decision aligns with business requirements and is economically efficient, we strongly recommend engaging in in-depth discussions with professional overhead crane suppliers or industry experts. They can provide detailed information about different crane types, helping you understand the technical specifications and performance indicators of each model.Advantages of DGCRANE Overhead Cranes
Personalized Consultation:
Our expert team can provide personalized consultations based on your specific requirements, assisting you in finding the most suitable overhead lifting solution for your scenario.Understanding Return on Investment:
Professional consultants not only help you understand the features and performance of each crane but also provide insights into long-term operating costs and potential return on investment.Safety and Efficiency:
Ensure that the selected crane meets the highest safety standards while maintaining efficient operations.Support and Services:
Offered support and services include installation, training, maintenance, and repair services. Through detailed comparison and analysis in this article, we hope to empower you to make more informed decisions when choosing between single girder and double girder cranes. Remember, selecting the right overhead crane is crucial for improving your operational efficiency and safety. Do not hesitate to contact professional suppliers or consult experts to obtain the information and guidance you need!
bridge crane,double girder overhead cranes,eot crane,overhead crane,single girder overhead cranes