Crane Maintenance: Wire Rope Inspection
Wire ropes are subjected to constant stress and heavy loads during lifting operations. Over time, this can lead to wear, corrosion, and other forms of deterioration. Regular inspection of wire ropes is crucial to detect potential issues early on, ensuring the safety of personnel, preventing equipment failure, and minimizing downtime.
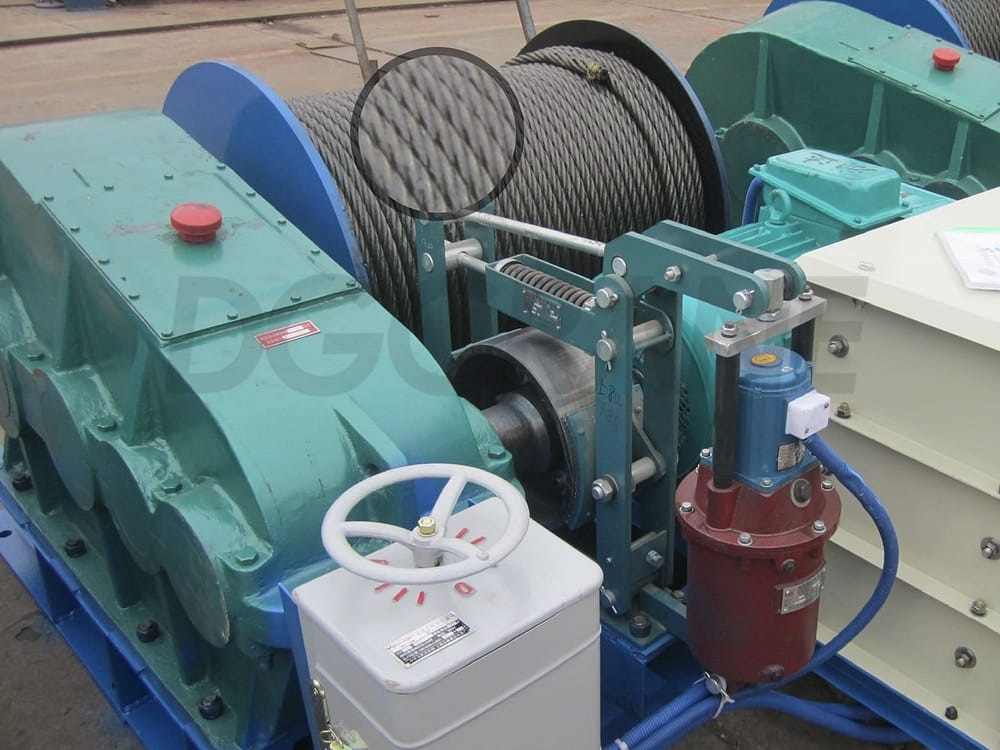 Wire Rope of DGCRANE’s Electric Winch
Wire Rope of DGCRANE’s Electric Winch
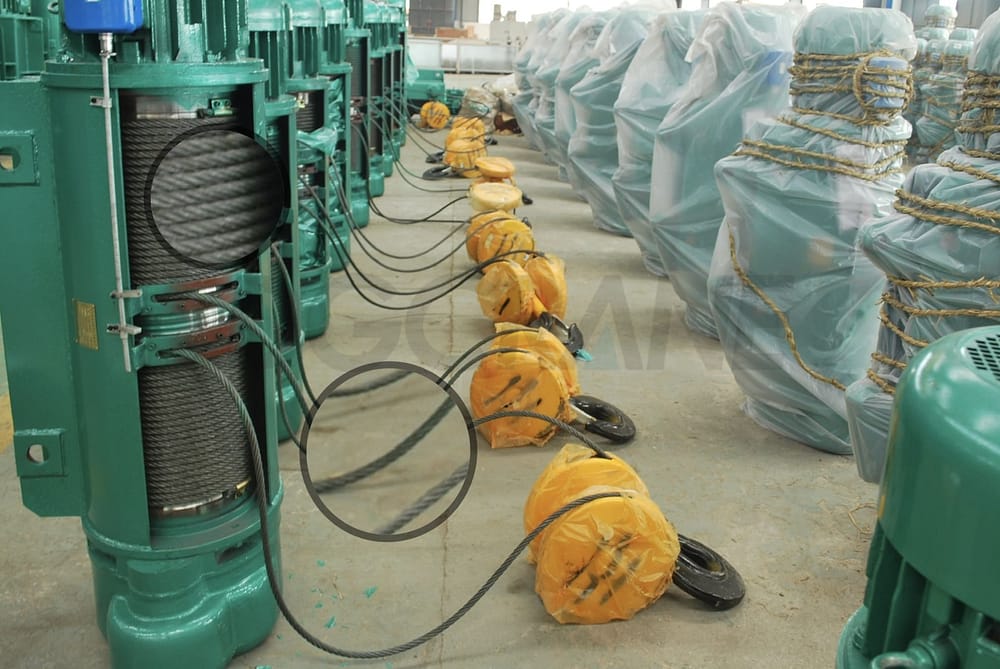 Wire Rope of DGCRANE’s CD1 Electric Hoist
Wire Rope of DGCRANE’s CD1 Electric Hoist
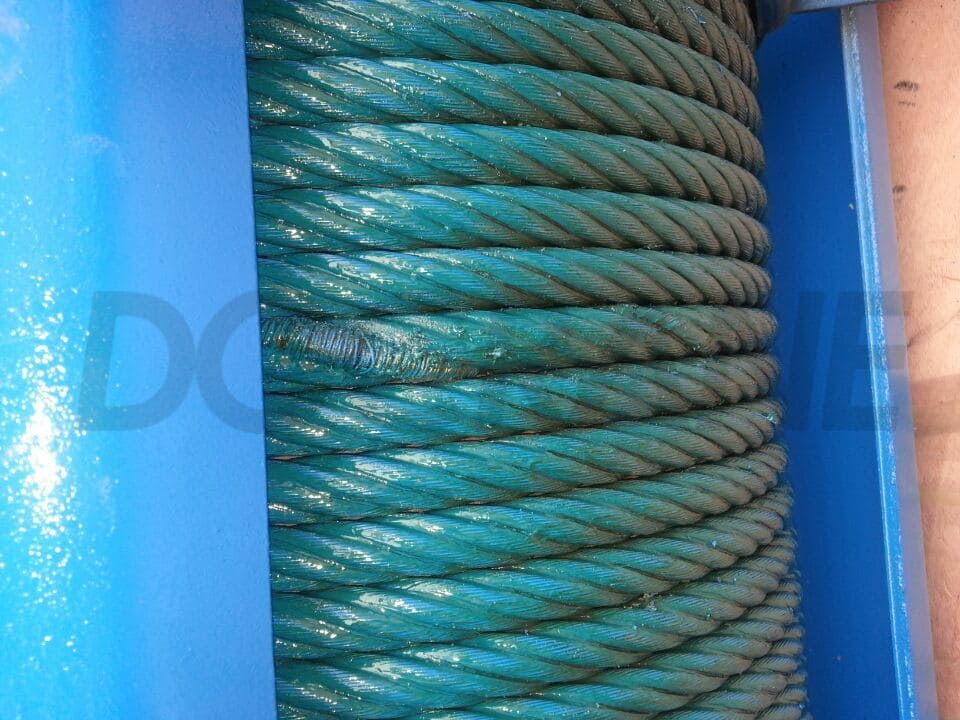
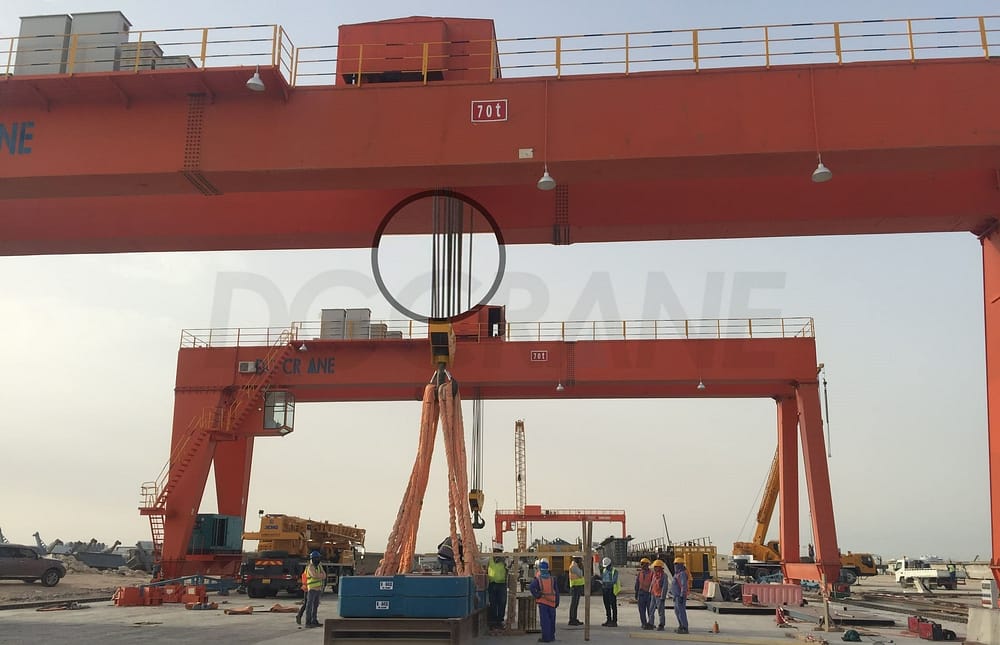 Wire Rope of DGCRANE’s 70T Gantry Crane Exported to Qatar
Wire Rope of DGCRANE’s 70T Gantry Crane Exported to Qatar
Common Diameter of Wire Rope for Electric Hoist with Different Rated Load
- Rated Load: 0.5t; Diameter: 4.76/5mm
- Rated Load: 0.5t; Diameter: 4.76/5mm
- Rated Load: 1t; Diameter: 7.7mm
- Rated Load: 2t; Diameter: 11mm
- Rated Load: 3t; Diameter: 13mm
- Rated Load: 5t; Diameter: 15mm
- Rated Load: 10t; Diameter: 17.5mm
- Rated Load: 20t; Diameter: 19.5mm
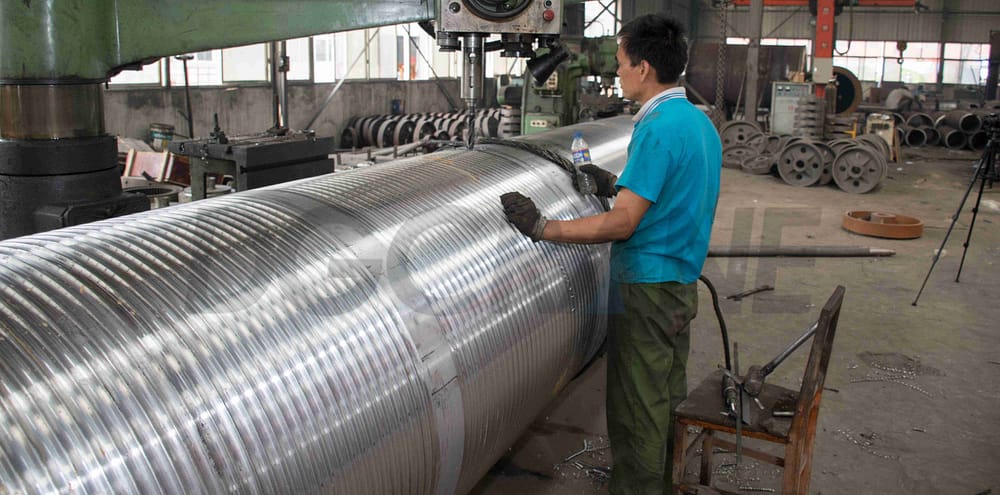 DGCRANE’s Expert Testing Wire Rope and Drum: Wire Rope always used with Drums
DGCRANE’s Expert Testing Wire Rope and Drum: Wire Rope always used with Drums
Every concrete situation should be specifically analyzed. Wire rope design varies from the customers’ lifting needs and other factors. See more about wire rope usage in our CASES datials, for example, 1 Set JM8T Electric Winch Order from Vietnam.
Common Causes of Wire Rope Deterioration
Several factors contribute to wire rope deterioration, including:
 Our Customers’ Damaged Wire Rope
Our Customers’ Damaged Wire Rope
- Fatigue from cyclic loading
- Corrosion and rust
- Overloading
- Abrasion and wear
- Incorrect installation or maintenance
Types of Inspections
- Visual Inspection: Visual inspection is the most basic form of wire rope inspection and can often reveal obvious signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. It involves visually examining the entire length of the rope, paying close attention to critical areas such as end connections and sheaves.
- Magnetic Particle Inspection: Magnetic particle inspection utilizes magnetic fields and iron particles to identify surface and near-surface defects in wire ropes. This method is particularly effective in detecting cracks, fractures, and other forms of hidden damage that may not be visible to the naked eye.
- Ultrasonic Testing: Ultrasonic testing involves the use of high-frequency sound waves to evaluate the internal condition of wire ropes. By analyzing the reflected sound waves, inspectors can identify internal flaws, such as broken wires or corrosion, without the need for dismantling the rope.
Preparing for a Wire Rope Inspection
Before conducting a wire rope inspection, certain preparations must be made:
- Necessary Equipment: Inspectors should have access to appropriate tools and equipment, including magnifying glasses, gauges, non-destructive testing devices, and personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and safety glasses.
- Safety Considerations: Wire rope inspections can involve working at heights and around heavy machinery. It is crucial to follow safety protocols, such as using fall protection equipment, wearing the appropriate PPE, and ensuring a secure work environment.
Wire Rope Inspection
Safe use of crane wire rope largely depends on proper maintenance and regular inspections. When instructions regarding the use of wire rope are not provided by the crane manufacturer, wire rope manufacturer, or supplier, inspections should be conducted according to the following guidelines.

I. Daily Inspection
- Regular visual inspections should be conducted on designated dates for the intended sections of the wire rope to identify general deterioration or mechanical damage. This inspection should also include the connection points between the wire rope and the crane.
- The correct positioning of the wire rope on the drum and sheaves should be checked to ensure it remains in its intended working position.
- Any observed changes in condition should be reported and further inspections of the wire rope should be conducted as per the requirements of regular inspections.
- Whenever rigging arrangements are altered, such as when the crane is relocated or rigging is reinstalled, visual inspections of the wire rope should be performed according to the provided guidelines.
II. Regular Inspection
1. General Guidelines
Regular inspections should be carried out by authorized personnel. The information obtained from these inspections is used to determine whether the crane wire rope can continue to be safely used until the next scheduled inspection or if immediate replacement is required within the specified timeframe.
2. Inspection Interval
The inspection interval for regular inspections should be determined by authorized personnel, taking into consideration the following factors:
- National regulations regarding wire rope applications
- Crane type and the environmental conditions at the worksite
- Working class of the equipment
- Previous inspection results
- Experience gained from inspecting similar crane wire ropes
- Duration of wire rope usage
- Frequency of usage
3. Inspection Scope
For each wire rope, a comprehensive inspection along its entire length should be conducted. For excessively long wire ropes, with approval from authorized personnel, inspections can be performed on a length that includes at least 5 wraps on the drum. Special attention should be given to critical areas and sections, including:
- The wire rope anchoring point on the drum
- Sections near the wire rope end fittings
- Segments passing through one or more sheaves
- Sections passing through load indicating devices
- Segments passing through hook sheave assemblies
4. End Fitting and Terminal Device Inspection
The wire rope near the end fittings, particularly the entry points into the terminal devices, should be inspected. This area is prone to wire breakage due to vibrations, impacts, and environmental factors like corrosion. Probing can be conducted to determine if the wires have become loose, indicating potential wire breakage within the terminal devices. Additionally, the end fittings should be checked for excessive deformation and wear. Protective sleeves and ferrules used for wire rope termination should also undergo visual inspection to detect any cracks or signs of potential slippage between the wire rope and the sleeves.
5. Inspection Records
After each regular inspection, authorized personnel should submit inspection records for the wire rope, indicating the maximum allowable time interval until the next inspection. It is advisable to maintain records of the wire rope’s regular inspections.
III. Post-Incident Inspection
If an accident occurs that may result in damage to the wire rope and its terminal devices, an inspection of the wire rope and its end fittings should be conducted before resuming operations. This inspection should follow the guidelines for regular inspections or as directed by authorized personnel.
In systems utilizing dual wire ropes for lifting mechanisms, even if only one wire rope becomes unusable, both ropes should be replaced together. This is due to the new wire rope being slightly thicker and having a different elongation rate, which affects the payout of both wire ropes on the drum.
IV. Inspection after Crane Inactivity
If a crane remains inactive for more than three months, regular inspections of the wire rope should be conducted according to the guidelines for scheduled inspections before resuming operations.
Rope Retirement Criteria
Rope retirement criteria define the limits of acceptable wear, damage, or deterioration that would render a wire rope unfit for further use. These criteria may vary depending on industry standards, manufacturer recommendations, and regulatory requirements.
The Role of Training and Certification
Wire rope inspection requires specialized knowledge and skills. Training programs and certifications are available to equip personnel with the necessary expertise to conduct thorough inspections and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Conclusion
In conclusion, crane wire rope inspection is a critical aspect of ensuring the safety and efficiency of crane operations. By implementing regular inspections using visual, magnetic particle, and ultrasonic testing methods, potential issues can be detected early on, allowing for timely maintenance and preventing catastrophic failures. With proper training, certification, and adherence to maintenance practices, industries can maximize the lifespan of cranes, hoists, or other lifting devices, and create a safer work environment.
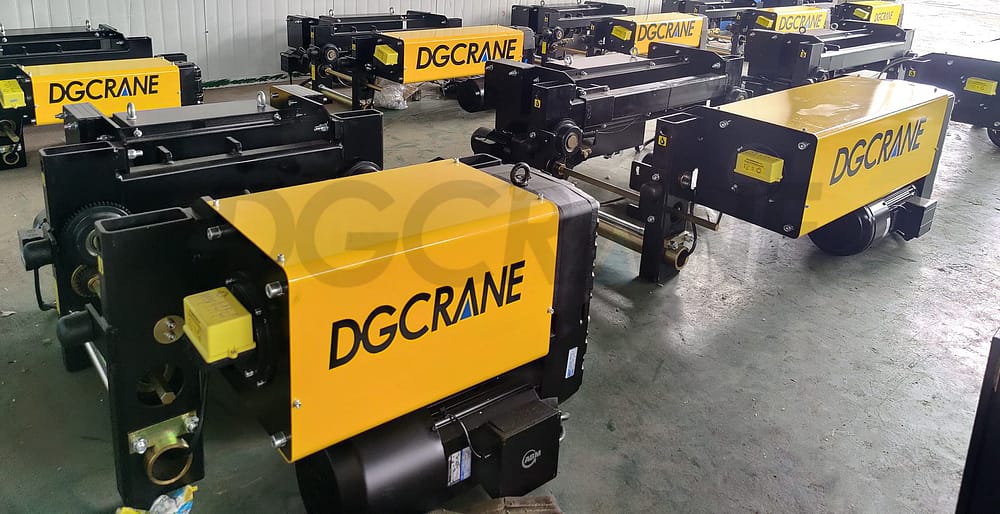 DGCRANE’s European Type Electric Wire Rope Hoist
DGCRANE’s European Type Electric Wire Rope Hoist
DGCRANE is a global reliable crane manufacturer. We provide high-quality cranes, custom accessories, and professional service. To get more information about crane and crane maintenance visit our homepage and contact us now!